- Psychological assessments ( IQ, SQ, EQ, Behavioral assessments)
- Skill training programme for children with Autism & other PDD
- Early intervention programme for children with delayed development.
- Structured, specialized education programme for children with learning disability and slow learners.
- Periodical Parental training and counseling.
- Linguistic development programme, music therapy, play therapy, sensory integration,audio – visual programmed to needy children.
- Vocational guidance and training to adult differently able.
- Awareness programmes to various target groups on autism & learning disability.
- Personality development programmes and mental health programme to various target groups.
Our beneficiaries

- Child with Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorder
- Child with Autistic Features and Autistic disorder.
- Children with developmental delay.
- Slow learner and learning disability.
- Child with Speech disorders.
- Children with Behavioral and scholastic problems.
- Children with emotional and social problems.
- Other associated conditions with PDD.
- Low vision, Down’s syndrome, and mild MR.
Methodology
“REACH” Method
Rakshna’s Early intervention for Children with Autism
REACH method was developed by a team of professionals headed by our psychologist Dr.Rani chakkaravarthy. Once in two years the team will gather to evaluate and upgrade the methodology. Feedbacks from the parents will be consider to increase the effectiveness of the method.

Introdution
Brain being the vital organ that propels our functioning, it would be productive and simple if the brain is trained in the forefront. The REACH instructions begin with making the child sense becomes aware, realize and interact with what is happening around him or her.
This therapy stresses on early identification and early intervention of children with Autism.
Children who begin interventions before the end of the critical period (3 years) show maximum developments than those intervened after the ceiling age.
Aim
The aim of REACH method is to enable the development of the child in all realms, in his or her own natural environment.
Objectives
The major objectives are:
- Early identification and early intervention of children with special needs.
- To make the parents as the secondary instructors.
- To enable the child to assimilate skills with set of instructions and guiding him to generalise the same in his own environment then and there.
- To maximise child’s potential through skill development instructions.
- To enable the child to utilize the skill achieved in varied environment.
- To enhance the quality of life through differential intervention into higher cognitive functions.

Beneficiaries
Children diagnosed to have ADHD, PDD, LD and Autism are the beneficiaries. REACH method can be used with some modifications to general developmental delay as well as to delayed speech.
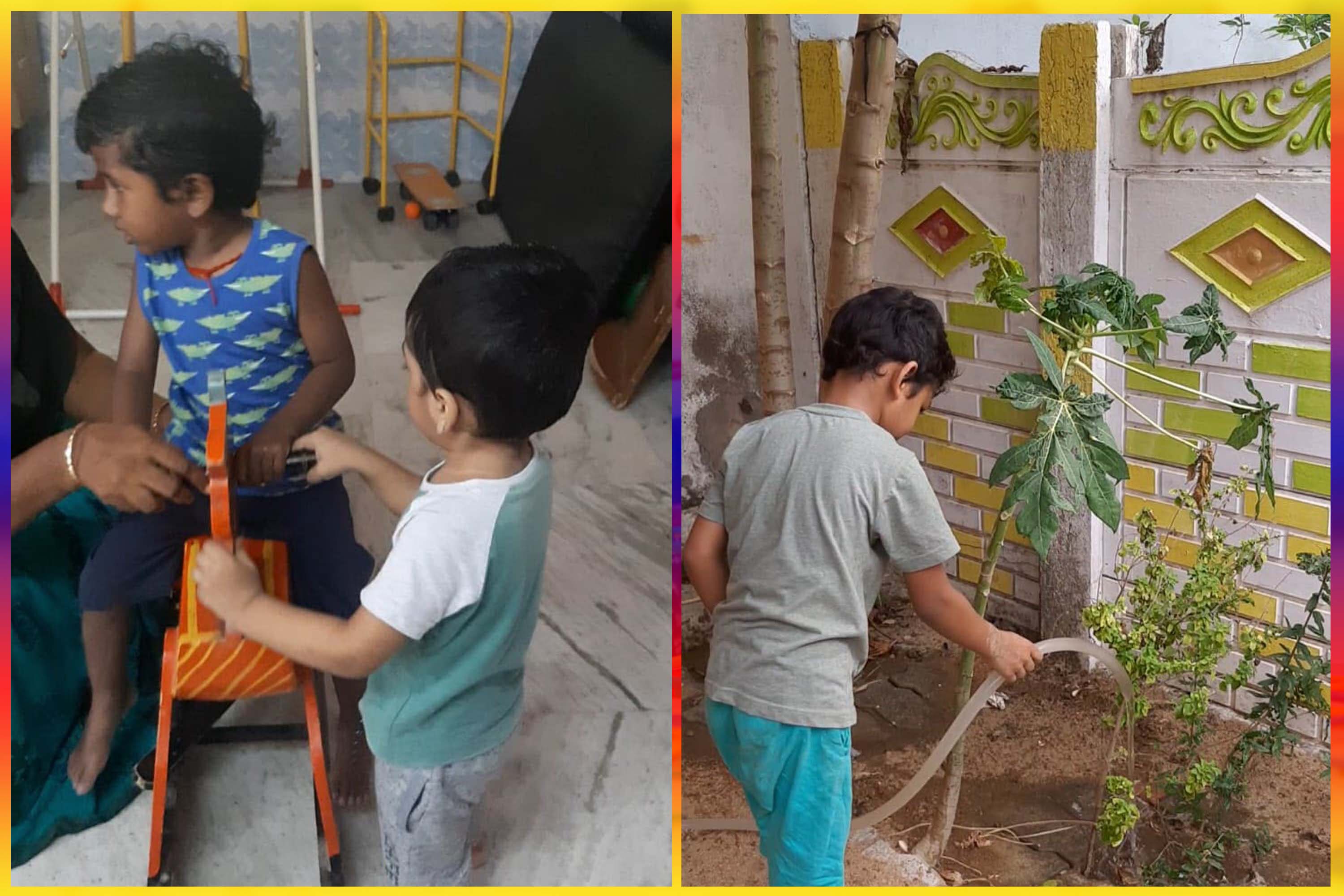


Core instruction Areas
- Developing eye contact:The child is enabled to develop, sustain eye contact and perceive visually from the surroundings. Childhood plays can help the children to attain eye contact.
- Sitting independently:The child is presented with activities of his or her interest continuously and is made to sit down with it. Initially, the child may need 10 – 15 activities for 30 minutes. Slowly, the activities can be reduced and the child learns to concentrate on a
particular activity for a prolonged period of time. - Developing attention and concentration skills: The activities for developing eye contact
simultaneously develop attention and slowly increase the span too. Now the child perceives and begins to learn. Involving children in day-to- day home activities will enable the child to increase attention. - Behaviour Modification:The behaviour modification techniques are employed then and there and the parents too are trained in the same.
- Developing imitation skills:This skill is very important for developing physical skills, speech and many other skills too. This skill stems out as the child sustains eye contact and develop attention.
- Receptive linguistic skills:The child is made to follow instructions from simple to complex instructions. The activities are planned in such a way that the child sits, develops eye contact, attend to the instruction, understand and execute what he or she is being instructed. First nouns are introduced, followed by verbs, adjectives, responding to questions through pointing and so forth.
- Receptive linguistic skills:The child is made to follow instructions from simple to complex instructions. The activities are planned in such a way that the child sits, develops eye contact, attend to the instruction, understand and execute what he or she is being instructed. First nouns are introduced, followed by verbs, adjectives, responding to questions through pointing and so forth.
- Expressive linguistic skills:Once the child’s comprehension of what is being spoken to him / her increases, the child may start uttering one or two words. This is the time, we give a tool to communicate – giving “yes” or “no” response to questions directed to him / her. For e.g. Do you want to eat dosa?…Then simultaneously more nouns are made to be articulated,followed by verbs, two word utterances, using adjectives, small sentences , asking questions and so forth. Oral motor and articulation exercises do precede the speech development.
- Development of self help skills:Age appropriate skills are taught then and there. It usually begins with developing bladder control, potty etc.
- Pre-academic and academic skill development:The activities chosen incorporate various concepts – colour, shape, size, vegetables, fruits, animals, birds etc and skills of categorisation, association too. The child is imparted with school readiness skills, beginning with fine motor coordination to colouring within a space, to turn taking and volunteering in a group.
- Social skill development:The child is given exposure through group activities and real experiences (by parents) to develop age appropriate social skills.
- Developing leisure time management:The child is exposed to wide of range of activities so that the child can decide what to do during leisure. This is very important as nil activity may lead to relapse of some extinct behaviour too.
- Higher cognitive skill development:As the child grows older, the child is imparted with analytical skills, applications skills and skills in divergent thinking. This is very essential as children should not become puppets and should be able to think, decide and perceive own interest and develop the quality of life he/ she is capable of achieving.